Seizure Types in the Trial Population
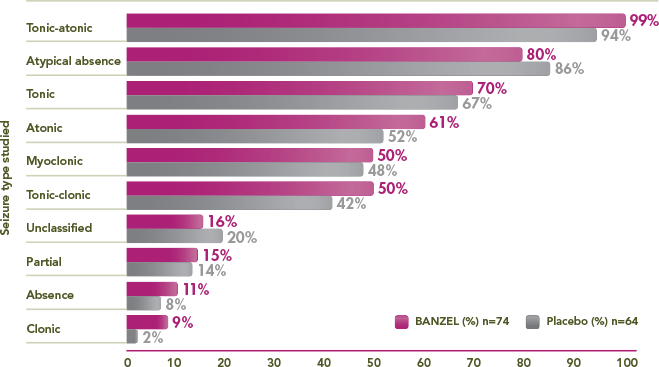
Seizure Types in the Trial Population
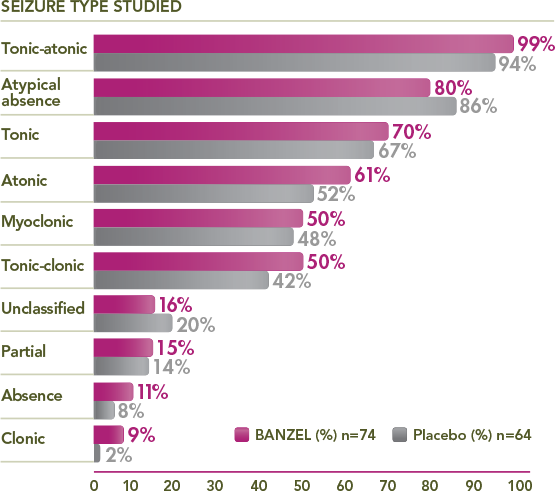
Percentage of trial patients with specific seizures at baseline1,3
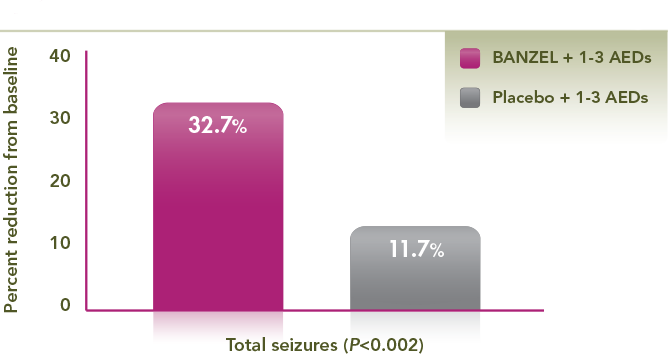
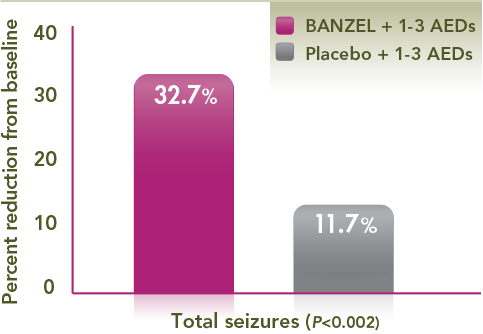
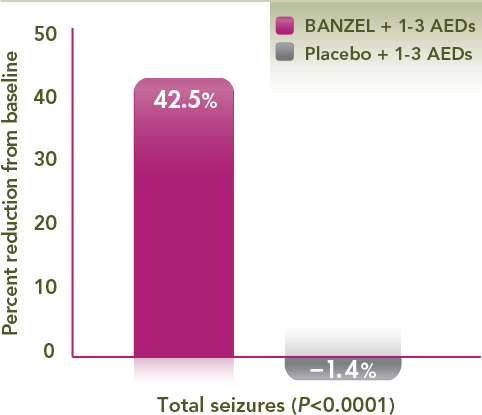
Adjunctive treatment with BANZEL® achieved a nearly three-fold median percent reduction in total seizures vs placebo
- 32.7% and 11.7% for BANZEL and placebo, respectively (P<0.002)
- Results vs placebo were statistically significant
Powerful efficacy in the reduction of tonic-atonic seizures (drop attacks)
Median percent reduction in tonic-atonic seizure frequency per 28 days relative to baseline*1,2
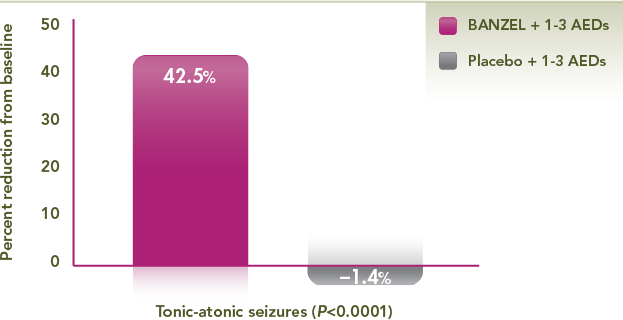
*Primary efficacy endpoint.
A 42.5% reduction in drop attacks in the BANZEL® group vs a 1.4% increase in the placebo group (P<0.0001)
- A primary efficacy endpoint, defined as percent change in the frequency of tonic-atonic (the sum of tonic and atonic seizures) per 28 days during the double-blind treatment phase
- Results vs placebo were statistically significant
- References: 1. Glauser et al. Rufinamide for generalized seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Neurology. 2008;70(21):1950-1958. 2. BANZEL® (rufinamide) prescribing information, Eisai Inc. 3. Data on file, Eisai Inc.
 Pivotal Trial Design Information
Pivotal Trial Design Information
- A 12-week, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial to assess the effectiveness of BANZEL (rufinamide) to reduce inadequately controlled seizures associated with LGS in patients (N=138, intent to treat) being treated with 1-3 concomitant stable-dose AEDs1-3
- The primary efficacy variables were the percent change in total seizure frequency per 28 days, the percent change in tonic-atonic (drop attacks) seizure frequency per 28 days, and the seizure severity rating from the parent/guardian global evaluation of the patient's condition1
- All 3 primary endpoints met the prespecified statistical criteria for effectiveness1